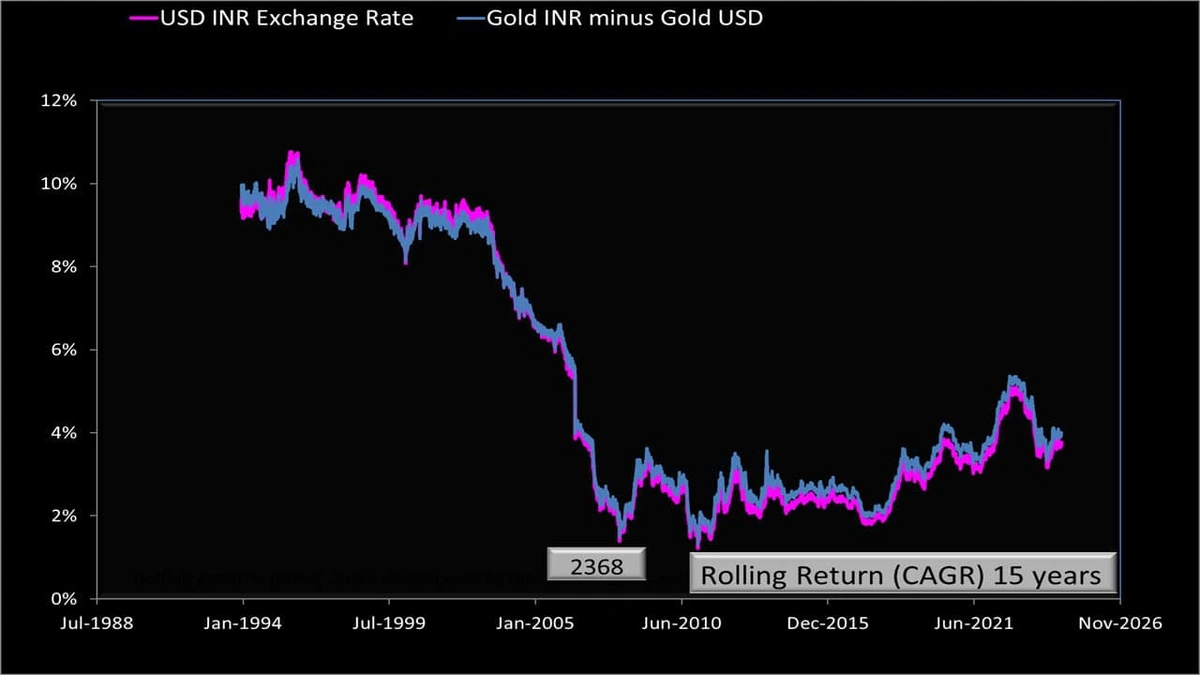
The Indian Rupee’s dance with the US Dollar is always a hot topic, isn’t it? We all feel it in our wallets – from the price of petrol to that new phone we’ve been eyeing. But why is the Rupee doing this tango in the first place? Let’s be honest, economics can feel like a maze. So, let’s break down the USD INR situation. I am going to try to explain the forces at play. This isn’t just about numbers; it’s about understanding the bigger picture and how it impacts you and me. It is about the India’s currency exchange rate.
Understanding the Global Factors
First things first, the global stage is a messy one. The strength of the US Dollar is often tied to its position as a safe haven currency. What does that mean? Well, when there’s global uncertainty – geopolitical tensions, economic slowdowns in other parts of the world, or even a pandemic – investors tend to flock to the Dollar. It’s seen as a safe bet, a place to park their money until the storm passes. This increased demand for the Dollar automatically makes it stronger against other currencies, including the Rupee. Think of it like everyone wanting the same brand of umbrella during a downpour; its price goes up! The dollar index (DXY) measures the dollar’s value against a basket of foreign currencies.
And it’s not just about global events. Actions taken by the US Federal Reserve (the Fed) have a massive impact. The Federal Reserve controls US monetary policy. The Fed’s decisions on interest rates, for instance, can send ripples across the world. When the Fed raises interest rates, it makes the Dollar more attractive to investors seeking higher returns. This, in turn, can lead to capital outflows from emerging markets like India, further weakening the Rupee. It’s a complex game of chess, and we’re all pawns – in a way. One can check the USD to INR conversion value on various financial platforms.
The Indian Economic Landscape
But the Rupee’s fate isn’t solely determined by external factors. What’s happening within India matters just as much. India’s economic growth rate, its inflation levels, and its current account deficit all play a crucial role. A high current account deficit (CAD), which essentially means India is importing more than it’s exporting, puts downward pressure on the Rupee. We’re spending more Dollars than we’re earning, creating a demand-supply imbalance. The higher the demand for the dollar, the weaker the Rupee becomes.
Here’s the thing: foreign investors are constantly evaluating the attractiveness of investing in India. If they perceive risks – whether it’s political instability, policy uncertainty, or concerns about economic reforms – they might pull their investments out, leading to a further depreciation of the Rupee. It’s all about confidence, and the perception of risk. Moreover, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) plays a crucial role. It intervenes in the foreign exchange market to manage the Rupee’s volatility. It uses India’s foreign exchange reserves to stabilize the exchange rate.
Geopolitical Instability and Crude Oil Prices
Let’s not forget geopolitics. Wars, conflicts, and political tensions in different parts of the world can trigger risk-off sentiment, strengthening the Dollar as investors seek safety. The Russia-Ukraine war, for example, sent shockwaves through the global economy, impacting currencies worldwide. Any escalation or de-escalation can significantly affect the Indian economy . These types of events can also drastically affect the demand for crude oil .
And speaking of oil, India is a major importer of crude oil. When global oil prices rise, India needs to spend more Dollars to buy the same amount of oil. This increased demand for Dollars puts pressure on the Rupee. The relationship between oil prices and the Rupee is a strong one. Keep an eye on global events, as they can affect the cost of your daily commute. Understanding these factors can help you anticipate potential fluctuations in the exchange rate .
RBI Intervention and its Impact
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) isn’t sitting idle while all this is happening. It steps in to manage the Rupee’s value, trying to prevent wild swings that could destabilize the economy. The RBI uses its foreign currency reserves to buy or sell Dollars in the market, influencing the supply and demand. Think of it as a balancing act – trying to keep the Rupee stable without depleting its reserves too much.
But the RBI’s intervention isn’t always a magic bullet. It’s a delicate balancing act. Too much intervention can deplete reserves and signal a lack of confidence. Too little, and the Rupee could spiral out of control. The RBI walks a tightrope, constantly assessing the situation and making calculated decisions. One of the most important things to check is the currency exchange rate and how it affects the Indian economy .
The Rupee’s fall against the USD is influenced by global and domestic factors. The strength of the US Dollar, India’s economic landscape, geopolitical instability, and RBI intervention all play key roles. Understanding these factors can help you better navigate the financial landscape. Want to learn more about small businesses? Here’s an article about Metroid Prime . And for further reading, consider checking this link about current stock market trends .
Interested in learning more about the U.S. Economy? Check out the Bureau of Economic Analysis . I initially thought this was straightforward, but then I realized how many layers there are!
FAQ
Frequently Asked Questions
Why does the USD strengthen during global crises?
The USD is considered a safe-haven currency. Investors worldwide tend to invest more in the dollar during times of uncertainty.
How does the Fed affect the Rupee?
When the Fed raises interest rates, it can attract investments to the US, thus strengthening the dollar and potentially weakening the Rupee.
What is the current account deficit, and how does it affect the Rupee?
A current account deficit means a country is importing more than it’s exporting, which can lead to downward pressure on the Rupee.
How does the RBI intervene in the foreign exchange market?
The RBI buys or sells dollars to manage the Rupee’s value, trying to prevent wild swings.
What role do crude oil prices play in the Rupee’s value?
As a major oil importer, India spends more dollars when oil prices rise, which can weaken the Rupee.
Are there any steps individuals can take to protect themselves during times of currency volatility?
Consider diversifying investments and staying informed about economic trends.
Disclaimer: ऊपर दिए गए विचार और सिफारिशें व्यक्तिगत विश्लेषकों या ब्रोकिंग कंपनियों की हैं, न कि "Finance Ghar" की। हम निवेशकों को सलाह देते हैं कि किसी भी निवेश निर्णय लेने से पहले प्रमाणित विशेषज्ञों से परामर्श करें। निवेश में जोखिम होता है और सही जानकारी के बिना निर्णय लेना हानिकारक हो सकता है।